Physical exfoliation of graphene and molybdenum disulfide sheets using conductive polyaniline: an efficient route for synthesizing unique, random-layered 3D ternary electrode materials†
Abstract
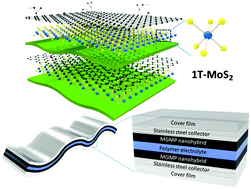
Vertically random-layered three-dimensional ternary nanohybrids were synthesized by combining graphene, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), and polyaniline (PANI) via a simple physical exfoliation process. During this process, PANI penetrates the interlayers of bulk MoS2 without the requirement for any additional chemical treatment, effectively dispersing MoS2 layers in the liquid phase. In addition, graphene, with several functional groups on its surface, and PANI convert the semiconducting trigonal prismatic phase of MoS2 to a metallic octahedrally coordinated phase, thereby enhancing the electrical conductivity. Moreover, the obtained nanohybrid has an open porous structure that facilitates electrolyte-mediated ion and charge transfer, which increases the effective surface area for electrochemical reactions and charge storage. The effect of different graphene, MoS2, and PANI contents on the electrical/electrochemical properties of the nanohybrids was investigated, and the optimal composition for the use of the nanohybrid as an electrode material was determined. Notably, the nanohybrid with a nominal graphene/MoS2/PANI weight ratio of 1 : 1 : 80 exhibited excellent electrochemical properties, exemplified by the prominent redox reaction, low charge transfer resistance, and high specific capacitance. Flexible all-solid-state capacitor cells employing the nanohybrid achieved a maximum capacitance of 162 F g−1, good flexibility, and good long-term cycling stability in two different electrolytes, i.e., acidic and neutral solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...