Constructing Li3VO4 nanoparticles anchored on crumpled reduced graphene oxide for high-power lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
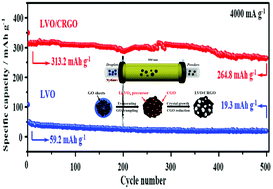
Li3VO4 is considered to be one of the most promising anode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) because of its outstanding safety performance and energy density. In this manuscript, hollow and spherical Li3VO4/crumpled reduced graphene oxide (LVO/CRGO) nanocomposites were formed by one-step and continuous spray pyrolysis with no need for further treatment. In this high-temperature gas phase process, the precursors of Li and V undergo a rapid chemical reaction, resulting in LVO nanoparticles anchored on the surface of graphene oxide. At the same time, the graphene oxide flakes are crumpled and reduced due to the droplet evaporation and a high-temperature reducing atmosphere in the reaction zone. The special three-dimensional (3D) architecture constructed by RGO sheets is beneficial for electrochemical performance owing to its preferable mechanical strength and superior electrical conductivity. When used as an anode, the LVO/CRGO nanocomposite exhibits extraordinary cycling and rate performance. It delivers an outstanding specific capacity of 487.5 mA h g−1 at 0.2C with less than 2% decay over 100 cycles. After 80 cycles at various specific currents from 0.1 to 60C, as the rate returned to 0.1C, the 5th specific capacity returns to 452.4 mA h g−1. Meanwhile, compared with general multiple-step methods, the one-step continuous spray pyrolysis method offers a facile, efficient and high-yielding alternative, which is meaningful and has potential in synthesizing other CRGO-based anode materials for LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...