Amino acid-inspired electrochemical recognition of phenylalanine enantiomers using amphoteric chitosan†
Abstract
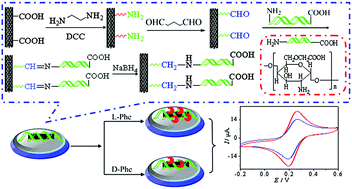
Inspired by amino acids with amphoteric groups for electrochemical enantiorecognition, amphoteric chitosan (ACCS) was prepared with chloroacetic acid and CS, and has perfect solubility in alkaline and acid solution, compared with CS. ACCS was linked to the ethylenediamine-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs–EA) through covalent bonding. Chiral interfaces were fabricated with MWCNTs–EA–ACCS and used for the electrochemical enantiorecognition of phenylalanine (Phe) enantiomers. The ACCS chiral interfaces showed excellent selectivity toward the Phe enantiomers. Also, the optimization of parameters such as pH, temperature and response time was carried out for the electrochemical recognition. Furthermore, the ACCS is capable of determining the percentage of enantiomers in mixed solutions. The electrochemical recognition of amino acid enantiomers with different functional groups was investigated, and it was found that the amphoteric functional groups of ACCS play an important role in the enantioselective discrimination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...