Enhancement in electrochemical performances of Li–S batteries by electrodeposition of sulfur on polyaniline–dodecyl benzene sulfonic acid–sulfuric acid (PANI–DBSA–H2SO4) honeycomb structure film
Abstract
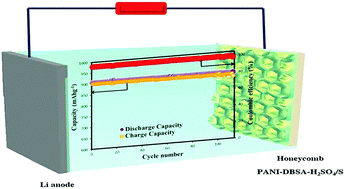
Recent developments in electric vehicles have heightened the need for improvement in the theoretical capacity of the rechargeable battery. In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries due to their high theoretical capacity of 1672 mAh g−1. Despite their high theoretical capacity, Li–S batteries have been plagued with fast capacity loss and dissolution and diffusion of the polysulfides. In this study, honeycomb polyaniline–dodecyl benzene sulfonic acid–sulfuric acid (hPANI–DBSA–H2SO4) was prepared using the breath figure (BF) method. Then, sulfur was electrodeposited on hPANI–DBSA–H2SO4 and used to investigate the electrochemical properties of the Li–S cells. hPANI–DBSA–H2SO4/S exhibited a higher capacity and excellent reversible capacity of 894 mAh g−1 after 100 cycles at 0.1C, and a columbic efficiency of 99.2% over 100 cycles was achieved. These results indicate that the honeycomb structure is likely to prevent the dissolution of the polysulfides. The findings suggest that this cathode can also be useful when applying Li–S cathodes for use in high capacity Li–S batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...