In situ synthesis of bismuth (Bi)/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanocomposites as high-capacity anode materials for a Mg-ion battery
Abstract
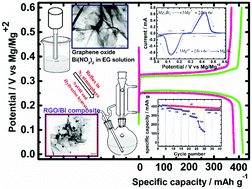
Herein, in situ reduction of bismuth and graphene oxide was performed by a solvothermal method under a N2 atmosphere, and the resulting Bi/RGO nanocomposites were used as an anode material for Mg-ion batteries. The nanocomposite of 60% Bi : 40% RGO is a beneficial anode material, delivering a discharge capacity as high as 413 and 372 mA h g−1 at the specific current of 39 mA g−1 in the 1st and 50th cycles, respectively. In addition, it shows high-rate capability with the discharge capacities of 381, 372, 354, 295, and 238 mA h g−1 at the specific currents of 53, 100, 200, 500, and 700 mA g−1, respectively. The better electrochemical performance of the nanocomposite is due to improvement in the electronic conductivity and significant reduction of volume changes during electrochemical cycling. This study demonstrates the bismuth (Bi)/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanocomposite as a promising high-capacity anode for magnesium-ion batteries with longer life cycle and high-rate performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...