The conjunction of a new ultrasonic-assisted dispersive solid-phase extraction method with HPLC-DAD for the trace determination of diazinon in biological and water media†
Abstract
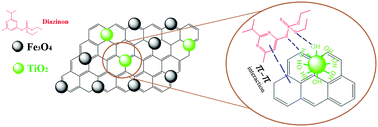
Herein, a new ultrasonic-assisted dispersive solid-phase extraction method using a TiO2/magnetic graphene-based sorbent in conjunction with the HPLC-diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) was successfully developed for the trace detection of diazinon. Initially, the TiO2/magnetic graphene-based sorbent was successfully synthesized and subsequently characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and elemental mapping techniques. Then, the sorbent was used for the sorption and extraction of diazinon mainly through π–π stacking hydrophobic interactions. Under the optimized conditions, the calibration curves were linear over the concentration range of 0.8–800 μg L−1 for urine, plasma and milk samples and 0.2–200 μg L−1 for water samples. The method detection limits were determined to be in the range of 0.05–0.3 μg L−1 based on a signal-to-noise ratio of 3 (S/N = 3). To test the extraction efficiency, the method was applied to various fortified real samples. The average recoveries obtained from the fortified samples varied between 92–104% with relative standard deviations of 6.1–10.2%. Finally, the method was determined to be effective for the analysis of diazinon in environmental and biological samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...