Ru(iii)–TMSO complexes containing azole-based ligands: synthesis and cytotoxicity study†
Abstract
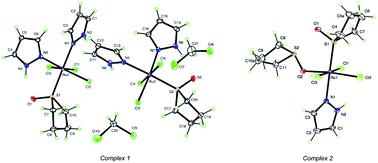
The reaction of mer-[RuCl3(S-TMSO)2(O-TMSO)] (TMSO = tetramethylene sulfoxide) with azoles (pyrazole = pzH and 3,5-dimethylpyrazole = dmpzH) in dichloromethane produced the complexes mer-[RuCl3(S-TMSO)(pzH)2] 1, mer-[RuCl3(S-TMSO)(O-TMSO)(pzH)] 2, mer-[RuCl3(S-TMSO)(dmpzH)2] 3, and mer-[RuCl3(S-TMSO)(O-TMSO)(dmpzH)] 4. These complexes were characterized using analytical, spectroscopic, and electrochemical techniques, as well as single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Cytotoxicity assays on NB-Nu-39, a human neuroblastoma cell line, revealed that compounds 3 and 4, bearing methyl groups at the 3- and 5-positions of the pyrazole ring, exhibited significant cytotoxic activity towards neuroblastoma cells with IC50 values of 14.5 μM and 12.9 μM, respectively. The IC50 value of NAMI-A was 12.4 μM, which is very close to that of 4. In contrast, compounds 1 and 2 exhibited no appreciable cytotoxic activity towards neuroblastoma cells (IC50 ≫ 100 μM). The lipophilicity of complexes 1–4 was measured by the shake-flask method to obtain the partition coefficient. These studies reveal that lipophilicity may be a determining factor in the anticancer activity and pharmacological behavior of these Ru(III) complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...