Novel visible light-driven Cu-based MOFs/Ag2O composite photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic activity toward the degradation of orange G: their photocatalytic mechanism and optimization study
Abstract
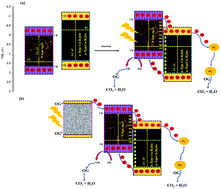
The present work is devoted to the synthesis of two visible light-driven Cu-based metal organic frameworks (Cu-H3-btc and Cu-H2-bdc) composited with Ag2O nanoparticles (Cu-H3-btc–Ag2O-NPs and Cu-H2-bdc–Ag2O-NPs, respectively) which are applied for the photocatalytic degradation of orange G (OG) dye in the presence of a blue LED. The successfully prepared photocatalysts are characterized via FT-IR, SEM, EDS, UV-vis DRS, PL, IES, XRD, TEM and HRTEM analysis. The obtained samples display superior photocatalytic activity due to their narrow band gap, good hole generating (OH radical generation) activity and low mass transfer resistance as well as the high surface area provided by the aggregation of Ag2O nanoparticles. This efficiently increases the escape probability of photogenerated electrons and the contact probability of photogenerated holes with the outer MOF material, assuring the superb photocatalytic activity and excellent stability of the as-prepared samples. The influence of operational factors such as initial OG concentration, solution pH, photocatalyst mass and irradiation time on the degradation efficiency individually and in combination are investigated using the central composite design (CCD). The optimum conditions for the photodegradation of OG by Cu-H3-btc–Ag2O-NPs are found to be 6.0, 80 min, 4.5 mg L−1 and 0.022 g and by Cu-H2-bdc–Ag2O-NPs 6.0, 80 min, 4.0 mg L−1 and 0.021 g L−1, corresponding to pH, irradiation time, OG concentration and photocatalyst mass, respectively. Under these optimum conditions, the photocatalytic degradation percentages of OG by Cu-H3-btc–Ag2O-NPs and Cu-H2-bdc–Ag2O-NPs with a desirability of 1.0 and 0.93 are 68.96% and 96.53%, respectively. The kinetics of the underlying process is successfully fitted to the Langmuir–Hinshelwood (L–H) kinetic model, while the apparent photocatalytic degradation rate constants (kr) and (KA) for Cu-H3-btc–Ag2O-NPs are determined to be 0.139 mg L min−1 and 0.060 L mg−1, and for Cu-H2-bdc–Ag2O-NPs 0.081 mg L min−1 and 0.146 L mg−1, respectively. Furthermore, the superb photocatalytic performance of the as-prepared photocatalysts remains almost constant after reuse or exposure under visible light.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...