A new triazoloquinoxaline ligand and its polymeric 1D silver(i) complex: synthesis, structure, and antimicrobial activity†
Abstract
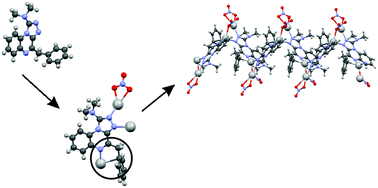
The organic ligand 4-benzyl-1-(N,N-dimethylamino)-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3a]quinoxaline 1 (L) and its polymeric silver(I) complex, [Ag2L(NO3)2]n (2), have been synthesized and characterized. The organic ligand 1 crystallizes in the triclinic space group P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) . The unit cell contains two parallel-stacked molecules. The complex [Ag2L(NO3)2]n (2) crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/n. The structure contains two different silver(I) ions. Ag(2) is coordinated by three oxygens (involving two nitrate groups) and to a nitrogen of the triazole ring of 1. These ligands form a strongly distorted tetrahedral, nearly planar coordination sphere. Ag(1) has an approximately tetrahedral geometry. It is bonded to one oxygen of a nitrate anion and a nitrogen of two different L, giving rise to an infinite chain structure. A final bond to Ag(1) involves the carbon of a phenyl group. It is more weakly bonded to the phenyl carbons on either side of this, so that the Ag(1)–phenyl bonding has aspects of an Ag–allyl bond. Ag(1) and Ag(2) participate in bonding to a common nitrate anion and alternate, the two distinct modes of bridging between them leading to a zig-zag chain structure. In addition to spectroscopic studies, the biological activities of the ligand and of the complex were scanned over a wide range of Gram positive and Gram negative flesh- and bone-eating bacteria. The results are discussed in comparison with well-known antibiotics.
. The unit cell contains two parallel-stacked molecules. The complex [Ag2L(NO3)2]n (2) crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/n. The structure contains two different silver(I) ions. Ag(2) is coordinated by three oxygens (involving two nitrate groups) and to a nitrogen of the triazole ring of 1. These ligands form a strongly distorted tetrahedral, nearly planar coordination sphere. Ag(1) has an approximately tetrahedral geometry. It is bonded to one oxygen of a nitrate anion and a nitrogen of two different L, giving rise to an infinite chain structure. A final bond to Ag(1) involves the carbon of a phenyl group. It is more weakly bonded to the phenyl carbons on either side of this, so that the Ag(1)–phenyl bonding has aspects of an Ag–allyl bond. Ag(1) and Ag(2) participate in bonding to a common nitrate anion and alternate, the two distinct modes of bridging between them leading to a zig-zag chain structure. In addition to spectroscopic studies, the biological activities of the ligand and of the complex were scanned over a wide range of Gram positive and Gram negative flesh- and bone-eating bacteria. The results are discussed in comparison with well-known antibiotics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...