Translation of protein charge and hydrophilicity to materials surface properties using thermal treatment in fluorous media†
Abstract
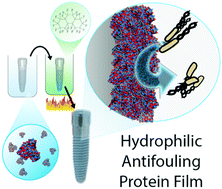
Protein-based materials provide an inherently biocompatible and sustainable platform for the generation of functional materials. Translating protein properties into protein films resistant to aqueous degradation is crucial for most applications such as tissue engineering and controlled drug delivery. Current methods to stabilize protein films use three main strategies: employing the relatively limited variety of naturally self-assembling proteins, using added cross-linkers or heat curing. While the cross-linking strategy generates functionally diverse structures, unreacted additives retained in cross-linked protein films can adversely affect their final behavior. Traditional heat curing results in hydrophobic surface and loss of protein inherent properties. We demonstrate here a scalable, additive-free, fluorous media assisted thermal treatment for the fabrication of stable, hydrophilic protein films. This approach is general in terms of protein building block, retaining much of their native structure and surface properties upon heating. We demonstrate the versatility of this strategy through fabrication of antifouling coatings on complex three-dimensional surfaces. The utility of these films as biomaterials is highlighted through the generation of highly biocompatible non-fouling surfaces and regulation of cellular adhesion through choice of protein precursor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...