Novel organophosphorus aminopyrimidines as unique structural DNA-targeting membrane active inhibitors towards drug-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus†
Abstract
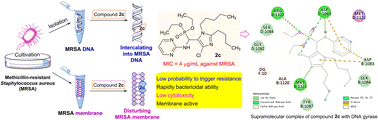
A series of novel unique structural organophosphorus aminopyrimidines were developed as potential DNA-targeting membrane active inhibitors through an efficient one-pot procedure from aldehydes, phosphonate and aminopyrimidine. The biological assay revealed that some of the prepared compounds displayed antibacterial activities. In particular, imidazole derivative 2c exhibited more potent inhibitory activity against MRSA with an MIC value of 4 μg mL−1 in comparison with the clinical drugs chloromycin and norfloxacin. Experiments revealed that the active molecule 2c had the ability to rapidly kill the tested strains without obviously triggering the development of bacterial resistance, showed low toxicity to L929 cells and could disturb the cell membrane. The molecular docking study discovered that compound 2c could bind with DNA gyrase via hydrogen bonds and other weak interactions. Further exploration disclosed that the active molecule 2c could also effectively intercalate into MRSA DNA and form a steady 2c–DNA supramolecular complex, which might further block DNA replication to exert powerful antibacterial effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...