Selective catalytic tailoring of the H unit in herbaceous lignin for methyl p-hydroxycinnamate production over metal-based ionic liquids†
Abstract
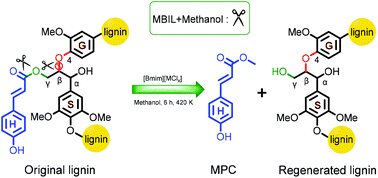
Selective valorization of lignin to achieve high value and commodity chemicals is attracting increasing attention. In this work, an efficient and reusable metal-based ionic liquid (MBIL) was developed for the selective tailoring of p-coumaric acid ester (pCA), a typical p-hydroxyphenyl (H) unit, into methyl p-hydroxycinnamate (MPC). Under optimized conditions and in the presence of catalyst [Bmim][FeCl4], a volatile aromatic product of 10.5 wt% was obtained, of which, 70.5% separated as pure MPC with an isolated yield of 71.1 mg g−1. FT-IR, 13C NMR, ANO and 2D HSQC demonstrated that the H unit was preferentially tailored from lignin, of which, 86.0 wt% of the H structure unit is cut off from lignin, with 70.6% being selectively converted to MPC. Further investigation demonstrated that MBIL prefers to tailor ester bonds compared to ether bonds using model compounds, and the superior catalytic ester bond cleavage performance exhibited by [Bmim][FeCl4] can be ascribed to the relatively narrow energy gap between the lignin ester bond and [FeCl4]− anion and to the comparatively low absolute binding energy between the cation and anion through DFT calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...