Dietary fibers, prebiotics, and exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria: potential health benefits with special regard to cholesterol-lowering effects
Abstract
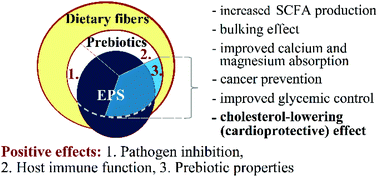
The gastrointestinal (GIT) microbiota, which plays a crucial role in human health, is influenced by a number of factors including diet. Consumption of specific dietary ingredients, such as dietary fibers and prebiotics, is an avenue by which the microbiota can be positively modulated. These substances may also reduce serum cholesterol levels through various mechanisms. Interest has increased in methods of reducing blood cholesterol level, because dyslipidemia is recognized as a contributory risk factor for the development of cardiovascular diseases. Several drugs have been developed for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia; however, undesirable side effects were observed, which have caused concerns about their long-term therapeutic use. Alternatively, many nonpharmacological approaches were tested to reduce elevated serum cholesterol levels. Dietary fibers and prebiotics have particularly beneficial effects on the GIT microbiome, and can also reduce serum cholesterol level through various mechanisms. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are potentially capable of synthesizing different polysaccharides, e.g. exopolysaccharides (EPS), which may play a role as prebiotics. LAB-based EPS have the potential to affect the gastrointestinal microbiome and reduce cholesterol. However, as dietary fibers comprise a complex group of substances with remarkably diverse structures, properties, and impacts, EPS also differ greatly and show a multitude of beneficial health effects. This review discusses the current knowledge related to the effects of dietary fibers and prebiotics on the human GIT microbiome, the prebiotic properties of EPS produced by LAB, and the health-promoting benefits of these polymers with special emphasis being given to cholesterol lowering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...