Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM10 alleviating oxidative stress and restoring the gut microbiota in d-galactose-induced aging mice
Abstract
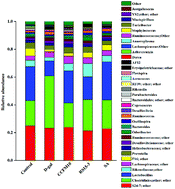
Oxidative stress and its correlation with degenerative diseases have been attracting wide attention. In the present study, Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) CCFM10 and RS15-3 were examined for their abilities to resist oxidative stress in D-galactose (D-gal)-exposed mice. Both strains significantly reversed the changes of hepatic total antioxidant capacity, catalase activity and glutathione content induced by D-gal. The antioxidative abilities of CCFM10 were higher than those of RS15-3. Moreover, the composition of the mice microbiota was changed by D-gal injection, which was characterized by the up-regulated ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes. At the genus level, the relative abundance of Lactobacillus reduced and the proportion of one genus of Clostridiales increased. However, in probiotic groups, the composition of the microbiota was similar to that of the control group at the phylum and the genus levels, suggesting that probiotic administration can restore the microbiota. Our study suggests that the protective effects of L. plantarum strains on the host microbiota could be one of the mechanisms of their resistance to oxidative stress. Besides this, through comparing the antioxidative capacity of two strains, we also found that the antioxidative capacity of L. plantarum might be strain-specific.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...