Quercetin induces the selective uptake of HDL-cholesterol via promoting SR-BI expression and the activation of the PPARγ/LXRα pathway†
Abstract
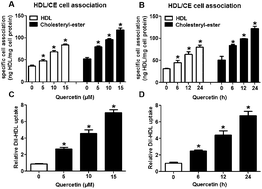
Reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) is the process to deliver cholesterol to the liver for further excretion and involves scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI)-mediated selective lipid uptake (SLU) from high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). The up-regulation of hepatic SR-BI expression accelerates HDL-C clearance in circulation and impedes the development of atherosclerosis (AS). In the present study, we explored the modulation of hepatic SR-BI expression and SR-BI-mediated SLU by quercetin, a natural flavonoid compound in the diet with a favorable role in cardiovascular disorders. We found that quercetin significantly increased the expression level of SR-BI in HepG2 cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Besides, quercetin had stimulatory effects on the binding of 1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate (Dil)-labeled HDL to hepatocytes and 125I/3H-CE-HDL association. Treatment with small interfering RNA (siRNA) or SR-BI specific inhibitor, BLT-1, inhibited quercetin-induced Dil-HDL binding and selective HDL-C uptake. Treatment with quercetin increased both proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and liver X receptor α (LXRα) levels. Additionally, the quercetin-induced expression of SR-BI, Dil-HDL binding and the selective uptake of HDL-C were significantly attenuated by treatment with PPARγ siRNA, LXRα siRNA, and their antagonists, respectively. In C57BL/6 mice, quercetin administration potently increased SR-BI, PPARγ and LXRα levels and lipid accumulation in the liver. Altogether, our results suggest that quercetin-induced up-regulation of SR-BI and subsequent lipid uptake in hepatocytes might contribute to its beneficial effects on cholesterol homeostasis and atherogenesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...