Biological leaching of metal contaminated substrates from a passive bioreactor treating mine drainage
Abstract
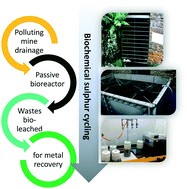
A proof of concept study is presented, using acid mine drainage (AMD) to leach metals (Zn, Cd, Ni, Mn, Fe, Pb, Cu) from a passive treatment system substrate. The substrate, taken from a sulphate-reducing bioreactor treating mine drainage at another site, was heavily contaminated with metals and could not be disposed of in landfill under UK regulations. Laboratory scale batch leaching experiments were conducted under aerobic conditions, in order to harness microbial sulphur oxidation to generate sulphuric acid and re-mobilise metals. Acid mine drainage, normally considered to be waste or an environmental liability, was used as a microbial inoculum and leach solution for the experiments, with added zero-valent sulphur as a supplementary nutrient source for sulphur oxidising bacteria. The initial reactor pH of 4.0 decreased to ≤2.8 in inoculated reactors, whereas the final pH of the sterile controls was 4.1. Metals data showed removal efficiencies of 71–100% for Zn, Cd, Ni and Mn in inoculated reactors upon completion of the 1600 hour leach period. These findings suggest that AMD can be used as a convenient leach solution and inoculum for the leaching of these metals from spent bioreactor treatment system substrates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...