Iodine soil dynamics and methods of measurement: a review†
Abstract
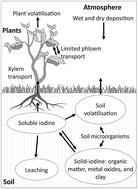
Iodine is an essential micronutrient for human health: insufficient intake can have multiple effects on development and growth, affecting approximately 1.9 billion people worldwide. Previous reviews have focussed on iodine analysis in environmental and biological samples, however, no such review exists for the determination of iodine fractionation and speciation in soils. This article reviews the geodynamics of both stable 127I and the long-lived isotope 129I (t1/2 = 15.7 million years), alongside the analytical methods for determining iodine concentrations in soils, including consideration of sample preparation. The ability to measure total iodine concentration in soils has developed significantly from rudimentary spectrophotometric analysis methods to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Analysis with ICP-MS has been reported as the best method for determining iodine concentrations in a range of environmental samples and soils due to developments in extraction procedures and sensitivity, with extremely good detection limits typically <μg L−1. The ability of ICP-MS to measure iodine and its capabilities to couple on-line separation tools has the significance to develop the understanding of iodine geodynamics. In addition, nuclear-related analysis and recent synchrotron light source analysis are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...