A highly stabilized nickel-rich cathode material by nanoscale epitaxy control for high-energy lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
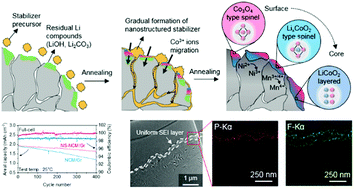
Advanced surface engineering of nickel-rich cathode materials greatly enhances their structural/thermal stability. However, their application into lithium-ion full-cells still faces challenges, such as the unstable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer on the anode. Herein, we reveal that the degradation of battery cycle life is caused by the release of divalent nickel ions from the LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathode and the formation of nickel metal particles on the graphite anode surface, deteriorating the anode SEI layer and its structural integrity. On the basis of this finding, we demonstrate a stable lithium-ion battery by modifying the cathode surface by creating a nanostructured stabilizer with an epitaxial structure that enhances the morphological robustness. During cycling, the nickel defects in the cathode are significantly suppressed, preventing nickel ion crossover. In particular, the anode SEI layer maintains a uniform and dense structure, leading to outstanding cycling stability in the full-cell with a capacity retention of ∼86% after 400 cycles at 25 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...