A paraelectric–ferroelectric phase transition of an organically templated zinc oxalate coordination polymer†
Abstract
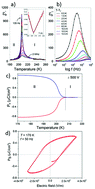
Water-presence dependent switchable ferroelectricity was discovered in the hybrid organic–inorganic zinc oxalate 1D coordination polymer (DABCOH2)[Zn(C2O4)2]·3H2O (DZnOH, where DABCOH2: diprotonated 1.4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane). The compound undergoes a reversible para–ferroelectric phase transition at 207 K from room temperature centrosymmetric phase I (space group P21/n) to low-temperature non-centrosymmetric phase II (space group P21). The microscopic mechanism of the phase transition is directly associated with the reconstruction of the hydrogen-bond network. On heating, the crystals exhibit a reversible single-crystal to single-crystal transformation concerned with the removal of all water molecules giving anhydrous DABCO zinc oxalate (DABCOH2)[Zn(C2O4)2] (DZnO). The dehydrated compound does not show ferroelectric properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...