Efficient and robust photocatalysts based on {P2W18} modified by an Ag complex†
Abstract
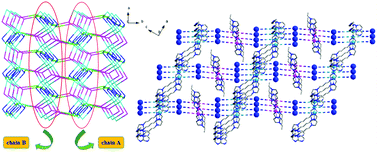
Two novel Wells–Dawson polyoxometalate-based compounds, (H2bimb)2[{Ag1.5(bimb)1.5}(P2W18O62)] (1), (H2bimb)2[Ag(bimb)]0.5[Ag(eim)2]0.5[P2W18O62]·H3O (2) (bimb = 1,4-bis(imidazole-l-yl)butane, eim = ethyl(imidazole)), have been synthesized under hydrothermal conditions and characterized by IR, thermogravimetric, XRD and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analyses. In compound 1, two “U”-type bimb ligands are connected together via π interactions of Ag–C to form a ring unit. The ring unit alternately links with the “Z”-type bimb via an Ag–N bond to form an infinite Z-shaped {Ag4(bimb)3}n chain. The adjacent two {P2W18} clusters bonded to two Ag1 ions on two adjacent Z-shaped chains to form an inorganic dimer linker, which further joins the Z-shaped chains together, resulting in unique organic–inorganic alternating 2-D layers. Adjacent 2D layers are further aggregated together via Ag–O bonds between the Dawson cluster and the Z-type chain on different layers to yield a 3-D network with a new topology {103}2{10}{4·102}4{42·104}2. In compound 2, the eim ligand was synthesized in situ from bimb, which acts as a small molecular ligand to alter the structure and adjust the catalytic activity of compound 2. Each Ag2 connects with the bimb ligand to form a linear {Ag(bimb)} chain. Adjacent chains are bonded together via the bimb ligand to generate a supermolecule 2-D layer, in which a Dawson dimer cluster as a guest molecule is embedded in both sides of the layer through supermolecule interactions. Such 2-D layers are further supported by Ag(eim)2 units leading to 3D supermolecule nets. In addition, the compounds exhibit excellent electrocatalytic behavior and better photocatalytic degradation capability for typical dyes than other Wells–Dawson POMs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...