Azobenzene-based solar thermal fuels: design, properties, and applications
Abstract
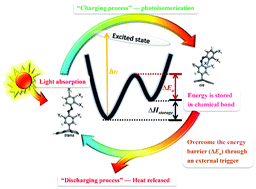
Development of renewable energy technologies has been a significant area of research amongst scientists with the aim of attaining a sustainable world society. Solar thermal fuels that can capture, convert, store, and release solar energy in the form of heat through reversible photoisomerization of molecular photoswitches such as azobenzene derivatives are currently in the limelight of research. Herein, we provide a state-of-the-art account on the recent advancements in solar thermal fuels based on azobenzene photoswitches. We begin with an overview on the importance of azobenzene-based solar thermal fuels and their fundamentals. Then, we highlight the recent advances in diverse azobenzene materials for solar thermal fuels such as pure azobenzene derivatives, nanocarbon-templated azobenzene, and polymer-templated azobenzene. The basic design concepts of these advanced solar energy storage materials are discussed, and their promising applications are highlighted. We then introduce the recent endeavors in the molecular design of azobenzene derivatives toward efficient solar thermal fuels, and conclude with new perspectives on the future scope, opportunities and challenges. It is expected that continuous pioneering research involving scientists and engineers from diverse technological backgrounds could trigger the rapid advancement of this important interdisciplinary field, which embraces chemistry, physics, engineering, nanoscience, nanotechnology, materials science, polymer science, etc.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...