Single entity electrocatalysis: oxygen reduction mediated via methyl viologen doped Nafion nanoparticles†
Abstract
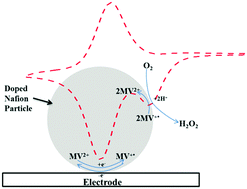
Nafion particles doped with methyl viologen are shown to be electrocatalytic towards oxygen reduction in aqueous solution when immobilised on a carbon electrode surface, with the formation of hydrogen peroxide. In this way an efficient homogeneous electron transfer mediator, methyl viologen, can be confined to act heterogeneously with the benefits of that type of process without losing effectiveness. Kinetic and mechanistic parameters are deduced from cyclic voltammetry and from single entity nano-impact experiments, and the process is shown to occur via electron transfer to dioxygen at the Nafion particle–solution interface with the initial formation of superoxide.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...