The synergetic effects of Ti3C2 MXene and Pt as co-catalysts for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution over g-C3N4†
Abstract
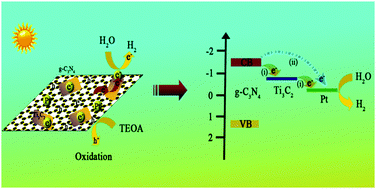
Co-catalyst loading provides an effective way to enhance the efficiency of photocatalysts for solar hydrogen production. From a sustainability point of view, it has immense scientific and technological values to explore more efficient co-catalytic systems by using multi-cocatalysts, because of potential synergetic effects between different components. Herein, the feasibility of using Ti3C2 MXene nanoparticles and Pt nanoclusters as dual co-catalysts to enhance the photoactivity of g-C3N4 for H2 production was investigated. Due to the improved electrical conductivity and increased reactive sites for photoreduction reactions, Ti3C2 and Pt co-modified photocatalysts exhibited a high photocatalytic hydrogen production activity of 5.1 mmol h−1 g−1. Compared to g-C3N4/Ti3C2 and g-C3N4/Pt, the 3- and 5-fold increased photoactivity demonstrated great potential of Ti3C2 MXene nanoparticles to construct high-performance photocatalysts. The synergetic effects between Ti3C2 and Pt were fundamentally investigated, indicating that the specific transfer of electrons not only contributed to the inhibited recombination of charge carriers but also resulted in good stability of heterostructured photocatalysts. Our results have demonstrated an approach worthy for the design and fabrication of high-efficiency heterostructures with superior photoactivity for hydrogen energy production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...