Comparison of charge transfer dynamics in polypyridyl ruthenium sensitizers for solar cells and water splitting systems†
Abstract
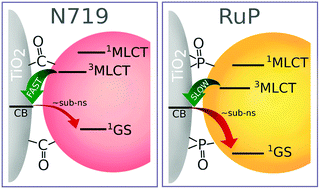
Standard ruthenium components of dye-sensitized solar cells (sensitizer N719) and dye-sensitized photoelectrochemical cells (sensitizer RuP and water oxidation catalyst RuOEC) are investigated in the same solar cell configuration to compare their photodynamics and charge separation efficiency. The samples are studied on time scales from femtoseconds to seconds by means of transient absorption, time-resolved emission and electrochemical impedance measurements. RuP shows significantly slower electron injection into a mesoporous titania electrode and enhanced fast (sub-ns) electron recombination with respect to those of N719. Moreover, RuOEC is found to be responsible for partial light absorption and electron injection with low efficiency. The obtained results reveal new insights into the reasons for the lower charge separation efficiency in water splitting systems with respect to that in solar cells. The important role of the initial processes occurring at the dye–titania interface within the first nanoseconds in this efficiency is emphasized.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...