Site-selective bond scission of methylbenzoate following core excitation
Abstract
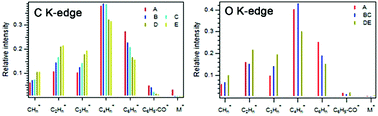
The chemical bond scission of methylbenzoate (C6H5CO2CH3) following core excitation at the C and O K edges was examined from partial ion yield measurements across these edges using synchrotron radiation. Site-specific scission of the C–O bonds was observed at both edges. Theoretical X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) were obtained using density functional theory. Peak assignments in the observed spectra were found to be consistent with the theory. From core-excited state dynamics calculations, an elongation of the C–O bond was predicted and provides an explanation of the observed partial ion yield enhancement of CH3+ and C6H5CO+ at the core-excited resonances at both edges.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...