Computational identification of the binding mechanism of a triple reuptake inhibitor amitifadine for the treatment of major depressive disorder†
Abstract
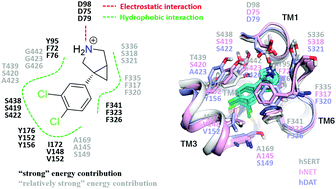
Amitifadine, the only drug ever clinically tested in Phase 3 for treating depression, is a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI) that simultaneously interacts with human monoamine transporters (MATs) including hSERT, hNET and hDAT. This novel multi-target strategy improves drug efficacy and reduces the toxic side effects of drugs. However, the binding modes accounting for amitifadine's polypharmacological mode of action are still elusive, and extensive exploration of the amitifadine–target interactions between amitifadine and MATs is urgently needed. In this study, a total of 0.63 μs molecular dynamics (MD) simulations with an explicit solvent as well as endpoint binding free energy (BFE) calculation were carried out. MD simulation results identified a shared binding mode involving eleven key residues at the S1 site of MATs for the binding of amitifadine, and the results of the BFE calculations were in good agreement with experimental reports. Moreover, by analyzing the per-residue energy contribution variation at the S1 site of three MATs and additional cross-mutagenesis simulations, the variation in the inhibition ratio of amitifadine between hSERT and two other MATs was discovered to mainly come from non-conserved residues (Y95, I172 and T439 in hNET and Y95, I172, A169 and T439 in hDAT). As the rational inhibition ratio of multi-target drugs among various therapeutic targets was found to be the key to their safety and tolerance, the findings of this study may further facilitate the rational design of more potent but less toxic multi-target antidepressant drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...