Tuning the electronic properties of bilayer group-IV monochalcogenides by stacking order, strain and an electric field: a computational study
Abstract
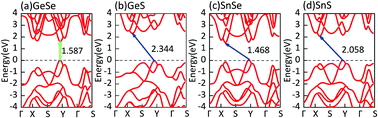
As the isoelectronic counterpart of phosphorene, monolayer group IV–VI binary MX (M = Ge, Sn; X = Se, S) compounds have drawn considerable attention in recent years. In this paper, we construct four high-symmetry stacking models for bilayer MX to tune their electronic properties. We systematically explore the dynamical and thermal stabilities of all bilayer MX. It is found that five of them are possible at room temperature. Then, we perform first-principles calculations to study how the bilayer structure affects their electronic properties. The results demonstrate that the electronic properties of MX materials can be modulated by forming bilayer structures. Their bandgap can be tuned over a wide range from 0.789 to 1.617 eV, and an indirect-to-direct transition occurs in three cases. Considering the flexibility of bilayer MX, we utilize in-plane uniaxial tensile strain to adjust their band structures and achieve much more indirect-to-direct bandgap transitions. The realization of direct bandgaps will be helpful for their application in next-generation high-efficiency modern nano-optoelectronic and photovoltaic devices. We also study the responses of different bilayer MX to an external vertical electric field. It is found that their bandgaps decrease rapidly with the increase of the electric field.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...