Tetranuclear Ni4 cubane complexes with high χT maxima: magneto-structural analysis†
Abstract
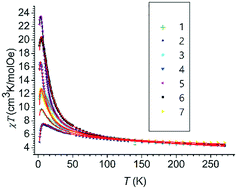
A series of seven tetranuclear Ni(II) cubane-like complexes of general formulae [Ni4L4(ROH)4] (1–3) and [Ni4L4(R1OH)x(R2OH)y] (x = y = 2 for complex 6, x = 1, y = 3 for complexes 4, 5 and 7; R = –C3H7, –C4H9, –C5H11; R1 and R2 = –CH3, –C2H5, –C3H7, –C4H9, –C5H11; L = N-(2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)salicylideneimine) were synthesized and their structural and magnetic properties were correlated in order to find out if the type of coordinated alcohol has any influence on magnetic properties. Their molecular structures reveal an octahedral coordination around nickel via five oxygen donor atoms and an imino nitrogen atom. Three out of the five oxygen atoms are derived from imine and one from the phenolate part of the Schiff base ligand, while the fifth one is derived from the neutral ROH ligand. Distortion of the cubane topology has been determined by Ni–O–Ni angle values and by O⋯Ni⋯O dihedral angle values. Intramolecular hydrogen bonds are various and rich, some are of the O–H⋯O type, spanning the cubane core and probably being one of the dominant causes of the distortion. Other weak intramolecular hydrogen bonds of the C–H⋯N type are present in complexes 1, 2, 3, 5 and 7. Very weak C–H⋯O intramolecular hydrogen bonds are responsible for the supramolecular architecture of complexes 2, 5 and 6. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds are present only in the crystal structures of complexes 2, 5 and 6. An unexpectedly high maximum of the χT(T) curve, above 20 emu K mol−1 Oe−1, is observed in some of the complexes. Significantly high χT maxima come from the quadratic spin–spin interactions depicted in the ZFS term as a consequence of the influence of the structural distortions and intermolecular interactions on the magnetic environment of Ni(II) ions. The influence of this contribution to the magnetic behaviour is revised in the known magneto-structural correlations between the values of the parameter of magnetic interaction J and the average Ni–O–Ni angle. The influence of the other structural characteristics, the average angle between O⋯Ni⋯O planes and the average angle between one O⋯Ni⋯O plane and the Ni⋯Ni vector, on the values of the parameter of magnetic interaction J is also analysed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...