In situ microscopy across scales for the characterization of crystal growth mechanisms: the case of europium oxalate
Abstract
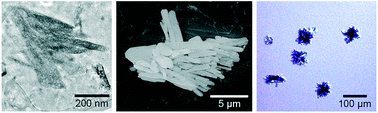
A better understanding of how production pathway affects the final product is required in order to produce targeted syntheses, but many of the classical ex situ techniques used for studying nanoparticle growth are unsuitable as stand-alone methods for identifying and characterizing growth mechanisms. Using a combination of high resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM), cryogenic TEM, liquid cell scanning electron microscopy, and optical microscopy we monitor europium oxalate growth over the range of nanometers to tens of micrometers and identify potential crystal growth pathways. Interpretation of the evolving crystallites reveals the significant impact of inhomogeneity in diffusion fields on diffusion limited crystal growth. We also compare the effects of stirring during crystal growth as an example of how changing processing conditions changes growth mechanisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
