Macrophage-targeting and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive nanopolyplexes mediate anti-inflammatory siRNA delivery against acute liver failure (ALF)†
Abstract
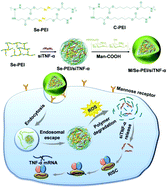
As one of the intractable challenges in the clinic, the treatment of acute liver failure (ALF) is limited due to high mortality and resource cost. RNA interference (RNAi) provides a new modality for the anti-inflammatory therapy of ALF, while its therapeutic efficacy is greatly hampered by the lack of effective carriers to cooperatively overcome the various systemic barriers. Herein, we developed macrophage-targeting and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive polyplexes to enable efficient systemic delivery of TNF-α siRNA (siTNF-α) to attenuate hepatic inflammation in mice bearing ALF. Se-PEI, obtained from the cross-linking of 600 Da polyethylenimine (PEI) via the ROS-responsive diselenide bond, was developed to condense siTNF-α, and the obtained polyplexes were further coated with carboxylated mannan (Man-COOH). Man-COOH coating allowed active targeting of polyplexes to macrophages with over-expressed mannose receptors (MRs), and it shielded the surface positive charges to enhance the serum stability of polyplexes. Se-PEI could be degraded by ROS in inflammatory macrophages to promote intracellular siRNA release to potentiate the gene knockdown efficiency, and in the meantime reduce the material cytotoxicity associated with high molecular weight. As such, i.v. injected Man-COOH/Se-PEI/siTNF-α polyplexes afforded notable TNF-α silencing by ∼80% in inflamed liver tissues at 500 μg siRNA per kg, and notably reduced serum TNF-α levels to achieve potent anti-inflammatory performance against ALF.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...