Isomeric control of the mechanical properties of supramolecular filament hydrogels†
Abstract
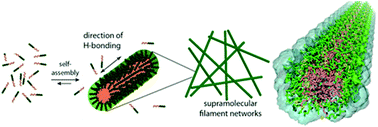
Supramolecular filament hydrogels are an emerging class of biomaterials that hold great promise for regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and drug delivery. However, fine-tuning of their bulk mechanical properties at the molecular level without altering their network structures remains a significant challenge. Here we report an isomeric strategy to construct amphiphilic peptides through the conjugation of isomeric hydrocarbons to influence the local viscoelastic properties of their resulting supramolecular hydrogels. In this case, the packing requirements of the chosen isomeric hydrocarbons within the supramolecular filaments are dictated by their atomic arrangements at the molecular and intermolecular levels. Atomistic molecular dynamics simulations suggest that this design strategy can subtly alter the molecular packing at the interface between the peptide domain and the hydrophobic core of the supramolecular assemblies, without changing both the filament width and morphology. Our results from wide-angle X-ray scattering and molecular simulations further confirm that alterations to the intermolecular packing at the interface impact the strength and degree of hydrogen bonding within the peptide domains. This subtle difference in the isomeric hydrocarbon design and their consequent packing difference led to variations in the persistence length of the individual supramolecular filaments. Microrheological analysis reveals that this difference in filament stiffness enables the fine-tuning of the mechanical properties of the hydrogel at the macroscopic scale. We believe that this isomeric platform provides an innovative method to tune the local viscoelastic properties of supramolecular polymeric hydrogels without necessarily altering their network structures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...