A non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on the CuS nanoflakes–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite†
Abstract
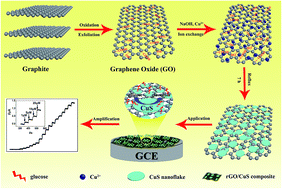
In this work, a copper sulfide nanoflakes–reduced graphene oxide (rGO/CuSNFs) nanocomposite has been successfully synthesized via one-pot hydrothermal treatment, where the reduction of GO and in situ generation of CuS nanoflakes occurred simultaneously. Subsequently, a nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor was fabricated based on the disposable rGO/CuSNFs nanocomposite for the highly sensitive and selective detection of glucose. The prepared rGO/CuSNFs nanocomposite was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, respectively. Under optimized conditions, the prepared enzymeless sensor exhibited remarkable catalytic activity toward the glucose oxidation with a fast response time of <6 s, a wide linear range from 1 to 2000 μM, a high sensitivity of 53.5 μM (cm2 mM)−1 and a low detection limit of 0.19 μM. Furthermore, the rGO/CuSNFs/GCE also showed the great reproducibility, the long-term storage stability and the excellent anti-interference ability for glucose sensing. In addition, the as-prepared sensor was applied to detect glucose in human urine and blood serum samples with satisfactory results, indicating that the rGO/CuSNFs nanocomposite is an extremely promising material for non-enzymatic glucose sensing in practical samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...