An amplification-free electrochemical detection of exosomal miRNA-21 in serum samples†
Abstract
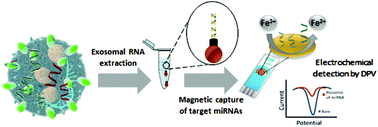
Recent evidence suggests that small non-coding RNAs such as microRNA (miRNA) encapsulated in exosomes represent an important mechanism of communication between the cells. Exosomal miRNAs play an important role in carcinogenesis via enhancing the cell to cell communication and targeting the cell growth molecular pathways which in turn facilitate metastasis in cancers. Despite progressive advances, the current methods for the exosomal miRNA detection mostly rely on labor-intensive sequencing approaches which are often prone to amplification bias and require costly and bulky equipment. Herein, we report an electrochemical approach for the detection of cancer-derived exosomal miRNAs in human serum samples by selectively isolating the target miRNA using magnetic beads pre-functionalized with capture probes and then directly adsorbing the targets onto a gold electrode surface. The level of adsorbed miRNA is detected electrochemically in the presence of an [Fe(CN)6]4−/3− redox system. This method enabled an excellent detection sensitivity of 1.0 pM with a relative standard deviation (%RSD) of <5.5% in cancer cells and serum samples (n = 8) collected from patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC). We believe that our approach could be useful in clinical settings for the quantification of exosomal miRNA in cancer patients.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...