Whole cell-SELEX of aptamers with a tyrosine-like side chain against live bacteria†
Abstract
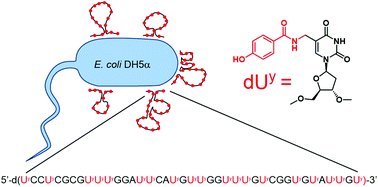
In an effort to expand the binding and recognition capabilities of aptamers, a nucleoside triphosphate modified with a phenol that mimics the side chain of tyrosine was used in the selection of DNA aptamers against live bacteria. Of multiple modified aptamers that were isolated against Escherichia coli DH5α cells, one aptamer displays high selectivity and affinity for the target cells and is greatly enriched for phenol-modified dU nucleotides (dUy, 47.5%). When the same sequences are synthesized with TTP, no binding is observed. Taken together, these findings highlight the value of using modified nucleotide triphosphates in aptamer selections and portends success in SELEX against an array of whole cells as targets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...