More accurate depiction of adsorption energy on transition metals using work function as one additional descriptor†
Abstract
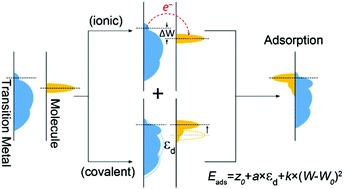
The reaction mechanism and properties of a catalytic process are primarily determined by the interactions between reacting species and catalysts. However, the interactions are often challenging to be experimentally measured, especially for unstable intermediates. Therefore, it is of significant importance to establish an exact relationship between chemical–catalyst interactions and catalyst parameters, which will allow calculation of these interactions and thus advance their mechanistic understanding. Herein we report the description of adsorption energy on transition metals by considering both ionic bonding and covalent bonding contributions and introduce the work function as one additional responsible parameter. We find that the adsorption energy can be more accurately described using a two-dimensional (2D) polynomial model, which shows a significant improvement compared with the current adsorption energy–d-band center linear correlation. We also demonstrate the utilization of this new 2D polynomial model to calculate oxygen binding energy of different transition metals to help understand their catalytic properties in oxygen reduction reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...