Chemically induced topological zero mode at graphene armchair edges†
Abstract
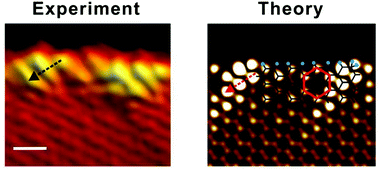
The electronic and magnetic properties of chemically modified graphene armchair edges are studied using a combination of tight-binding calculations, first-principles modelling, and low temperature scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) experiments. The atomically resolved STM images of the hydrogen etched graphitic edges suggest the presence of localized states at the Fermi level for certain armchair edges. We demonstrate theoretically that the topological zero-energy edge mode may emerge at armchair boundaries with asymmetrical chemical termination of the two outermost atoms in the unit cell. We particularly focus our attention on armchair edges terminated by various combinations of the hydrogen (H, H2) and methylene (CH2) groups. The inclusion of the spin component in our calculations reveals the appearance of π-electron-based magnetism at the armchair edges under consideration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...