Graphene flakes obtained by local electro-exfoliation of graphite with a STM tip†
Abstract
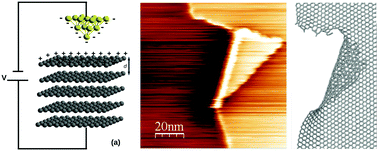
Graphite surfaces can be manipulated by several methods to create graphene structures of different shapes and sizes. Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) can be used to create these structures either through mechanical contact between the tip and the surface or through electro-exfoliation. In the latter, the mechanisms involved in the process of exfoliation at an applied voltage are not fully understood. Here, we show how a graphite surface can be locally exfoliated in a systematic manner by applying an electrostatic force with a STM tip at the edge of a terrace, forming triangular flakes several nanometers in length. We demonstrate, through experiments and simulations, how these flakes are created by a two-step process: first a voltage ramp must be applied at the edge of the terrace, and then the tip must be scanned perpendicular to the edge. Ab initio electrostatic calculations reveal that the presence of charges on the graphite surface weakens the interaction between layers allowing for exfoliation at voltages in the same range as those used experimentally. Molecular dynamics simulations show that a force applied locally on the edge of a step produces triangular flakes such as those observed under STM. Our results provide new insights into surface modification that can be extended to other layered materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...