Dynamic sandwich-type electrochemical assay for protein quantification and protein–protein interaction†
Abstract
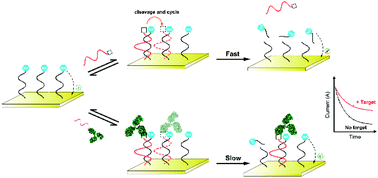
The study of protein–protein interactions (PPIs) plays an important role in the understanding of biological systems; however, the established methods for PPI analysis often involve cumbersome sample preparation, multiple detecting steps, and costly instruments. Here we report a versatile and sensitive electrochemical method based on PPI-induced distinctive migration behavior of DNA deoxyribozyme (DNAzyme) on an electrode surface. In this method, the cleavage activity of DNAzyme toward the substrate DNA modified on the electrode surface is inversely correlated with the hydrodynamic diameter of the macromolecule attached to it. By making full use of this principle in an inexpensive electrochemical format that is named the dynamic sandwich-type electrochemical assay (dSTEA), we can probe into the presence of large macromolecules in a single-step procedure. Moreover, we can not only detect sub-picomolar protein interaction events but also analyze the assembly of kinase in the whole cell extract. This novel signaling mechanism proposed in this work may broaden the applicability of DNAzyme-based electrochemical assays and it may also have great potential for applications in other interfacial sensor developments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...