Penetration and drug delivery of albumin nanoparticles into pancreatic multicellular tumor spheroids
Abstract
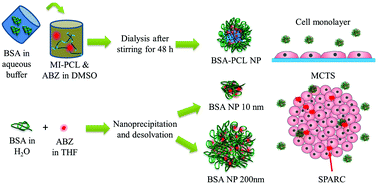
Albumin-based nanoparticles have been exploited as a useful carrier for the efficient delivery of anti-cancer drugs. In this study, albendazole was encapsulated into bovine serum albumin (BSA)–polycaprolactone (PCL) conjugates and the formed nanoparticles with a size about 100 nm were used to treat pancreatic carcinoma cells. In addition, two more types of albendazole-loaded BSA nanoparticles, 10 nm and 200 nm ones, were prepared using a desolvation method. The albendazole-loaded BSA nanoparticles were evaluated with both 2D cultured AsPC-1 cells and 3D multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTS). Their anti-tumor effects were also compared. BSA–PCL nanoparticles and 200 nm BSA nanoparticles showed noticeable cytotoxicity to 2D cultured AsPC-1 cells when compared to the free drug. The penetration of BSA–PCL nanoparticles and 200 nm BSA nanoparticles, especially the BSA–PCL nanoparticles, enabled effective delivery of albendazole into pancreatic MCTS. BSA–PCL nanoparticles also showed a better inhibition effect on the growth of pancreatic MCTS than the 200 nm counterpart. Although 10 nm BSA nanoparticles inhibited the growth of MCTS, the inhibitory effect was even less than that of free albendazole. In addition, it is also found that SPARC protein facilitates the penetration and drug delivery of albumin nanoparticle since treatment using anti-SPARC antibody decreased the efficacy of drug loaded BSA nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...