Carbon-incorporated Janus-type Ni2P/Ni hollow spheres for high performance hybrid supercapacitors†
Abstract
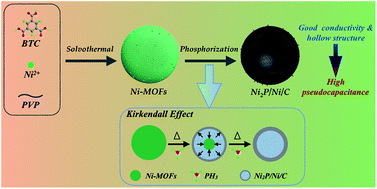
Transition metal phosphides, especially Ni2P, are of great interest as promising battery-type electrode materials for hybrid supercapacitors, but their poor electrical conductivity and porosity limit their application. Here, for the first time, the synthesis of carbon-incorporated Janus-type Ni2P/Ni hollow spheres (Ni2P/Ni/C) was reported via simultaneous carbonization and phosphorization of Ni-based metal–organic frameworks (Ni-MOFs). Their unique structural merits include the incorporated carbon content, Janus-type Ni2P/Ni nanocrystals, and high-porosity hollow structure, thus endowing them with a high specific surface area, good electrical conductivity and low density. As a result, the optimized Ni2P/Ni/C exhibits a remarkable specific capacitance of 1449 F g−1 at 1 A g−1 in 2 M KOH aqueous electrolyte in a three-electrode system. A hybrid supercapacitor device was fabricated by using Ni2P/Ni/C as the positive electrode and active carbon as the negative electrode, and it achieves a very high energy density of 32.02 W h kg−1 at a power density of 700 W kg−1 and a remarkable cycling stability (about 99% capacitance retention after 5000 cycles). The Ni2P/Ni/C should be one of the most promising electrode materials for hybrid supercapacitor application.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...