Improved hydrogen release from ammonia borane confined in microporous carbon with narrow pore size distribution†
Abstract
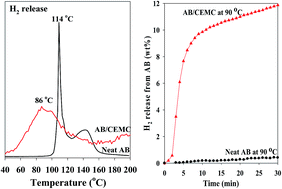
Ammonia borane is a promising hydrogen storage candidate due to its high hydrogen capacity and good stability at room temperature, but there are still some barriers to be overcome before it can be used for practical applications. We present the hydrogen release from ammonia borane confined in templated microporous carbon with extremely narrow pore size distribution. Compared with neat ammonia borane, the hydrogen release temperature of ammonia borane confined in microporous carbon with a pore size of 1.05 nm is significantly reduced, starting at 50 °C and with the peak dehydrogenation temperature centred at 86 °C. The dehydrogenation kinetics of ammonia borane confined in templated microporous carbon is significantly improved and by-products including ammonia and diborane are also completely prohibited without any catalysts involved. The remarkably fast hydrogen release rate and high hydrogen storage capacity from ammonia borane confined in microporous carbon are due to the dramatic decrease in the activation energy of ammonia borane. This has been so far the best performance among porous carbon materials used as the confinement scaffolds for ammonia borane in hydrogen storage, making AB confined in microporous carbon a very promising candidate for hydrogen storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...