N-Methylcarbamoyl azide: spectroscopy, X-ray structure and decomposition via methylcarbamoyl nitrene†
Abstract
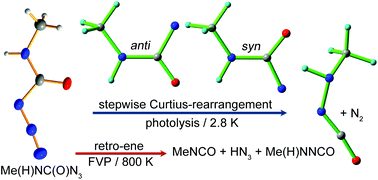
N-Methylcarbamoyl azide Me(H)NC(O)N3 has been synthesized and structurally characterized. Both N3 and CH3 groups in the molecule adopt a syn conformation with the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond. Upon flash vacuum pyrolysis at 800 K, the azide mainly decomposes into Me(H)NNCO/N2 and MeNCO/HN3 through Curtius-rearrangement and a retro-ene reaction, respectively. In contrast, 193 and 266 nm laser photolysis of Me(H)NC(O)N3 in cryogenic matrices (Ar, Ne, and N2) leads to stepwise Curtius-rearrangement via the intermediacy of carbamoylnitrene Me(H)NC(O)N, for which two conformers with the CH3 group being in syn and anti conformations to the C
O bond. Upon flash vacuum pyrolysis at 800 K, the azide mainly decomposes into Me(H)NNCO/N2 and MeNCO/HN3 through Curtius-rearrangement and a retro-ene reaction, respectively. In contrast, 193 and 266 nm laser photolysis of Me(H)NC(O)N3 in cryogenic matrices (Ar, Ne, and N2) leads to stepwise Curtius-rearrangement via the intermediacy of carbamoylnitrene Me(H)NC(O)N, for which two conformers with the CH3 group being in syn and anti conformations to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond have been unambiguously identified by matrix-isolation IR spectroscopy. Triplet multiplicity of Me(H)NC(O)N (|D/hc| = 1.57 cm−1 and |E/hc| = 0.012 cm−1) and another two carbamoylnitrenes H2NC(O)N (|D/hc| = 1.59 cm−1 and |E/hc| = 0.018 cm−1) and Me2NC(O)N (|D/hc| = 1.55 cm−1 and |E/hc| = 0.016 cm−1) has been further established by matrix-isolation EPR spectroscopy. Subsequent visible light irradiation (420–460 nm) of Me(H)NC(O)N results in the exclusive formation of Me(H)NNCO. The molecular structures of Me(H)NC(O)N3 and Me(H)NC(O)N, multiplicities of the nitrene, and the underlying mechanism for the decomposition of the azide are reasonably explained with quantum chemical calculations by utilizing the B3LYP, CBS-QB3, CCSD(T), and CASPT2 methods.
O bond have been unambiguously identified by matrix-isolation IR spectroscopy. Triplet multiplicity of Me(H)NC(O)N (|D/hc| = 1.57 cm−1 and |E/hc| = 0.012 cm−1) and another two carbamoylnitrenes H2NC(O)N (|D/hc| = 1.59 cm−1 and |E/hc| = 0.018 cm−1) and Me2NC(O)N (|D/hc| = 1.55 cm−1 and |E/hc| = 0.016 cm−1) has been further established by matrix-isolation EPR spectroscopy. Subsequent visible light irradiation (420–460 nm) of Me(H)NC(O)N results in the exclusive formation of Me(H)NNCO. The molecular structures of Me(H)NC(O)N3 and Me(H)NC(O)N, multiplicities of the nitrene, and the underlying mechanism for the decomposition of the azide are reasonably explained with quantum chemical calculations by utilizing the B3LYP, CBS-QB3, CCSD(T), and CASPT2 methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...