Simultaneously improving the mechanical properties and flame retardancy of polypropylene using functionalized carbon nanotubes by covalently wrapping flame retardants followed by linking polypropylene†
Abstract
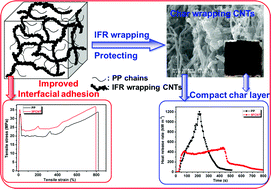
The fabrication of polymer nanocomposites with improved physical and chemical properties is a hot topic in the fields of materials and chemistry. In this work, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are functionalized through flame retardant wrapping and maleic anhydride polypropylene (PPMA) covalently attaching to achieve a compact char layer and strong interfacial adhesion. The resultant polypropylene (PP)/functionalized CNT (FCNT) composites show remarkably improved flame retardancy and mechanical properties. For example, with the incorporation of FCNTs, the mechanical properties of PP are largely improved, meanwhile the ductility is maintained. This is thanks to the strong interfacial adhesion between FCNTs and the PP matrix. In contrast, the elongation at break of the PP/CNT composites decreases seriously. More importantly, the flame retardancy of the PP/FCNT composites is much better than that of PP and the PP/CNT composites. The improved flame retardancy results from the fact that the flame retardant wrapping forms a char layer on the surface of the CNTs, which protects the CNTs from being destroyed during combustion. As a result, the quality of the residual char is improved. The flammability of the PP composites is strongly dependent on the residual char of the CNTs. The compact and continuous residual char of the FCNTs not only acts as the shield for heat transfer, but also hinders the migration of volatile decomposition products out of PP and the diffusion of oxygen into PP.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...