Multiwalled carbon nanotube supported Schiff base copper complex inorganic nanocomposite for enhanced electrochemical detection of dopamine†
Abstract
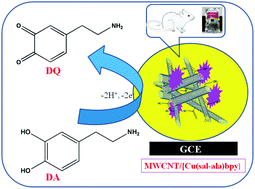
We have described a multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) supported [Cu(sal-ala)bpy] (sal-ala = salicylalanine-alanine, bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine) inorganic nanocomposite that was successfully prepared and applied for the selective detection of dopamine (DA). The prepared nanocomposite was characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), elemental analysis (EIS), UV-visible spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and IR-spectroscopy studies. Moreover, the electrochemical response of the nanocomposite was investigated using cyclic voltammetry (CV), amperometry (it) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) techniques. A MWCNT/[Cu(sal-ala)bpy] nanocomposite fabricated GCE electrode exhibited an enhanced electrochemical response towards the detection of DA with a high current response (Ip) and a low oxidation potential (Ep). The electrochemical response of DA oxidation at the Schiff base inorganic nanocomposite modified electrode is a surface controlled process. On the other hand, the electrocatalytic performance of the modified electrode shows a linear response range from 0.1 to 300 μM, with a detection limit of 0.16 μM and a sensitivity of 2.3455 μA μM−1 cm−2. In addition, the MWCNT/[Cu(sal-ala)bpy] nanocomposite modified GCE electrode had excellent stability, repeatability and reproducibility towards the detection of DA. Additionally, the practicability of the DA sensor was examined in rat serum and dopamine hydrochloride injection samples, and revealed acceptable recovery results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...