Increasing the solubility range of polyesters by tuning their microstructure with comonomers†
Abstract
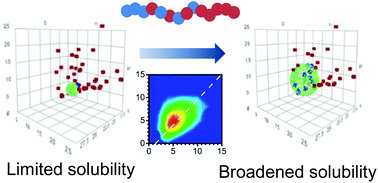
The solubility range of ω-pentadecalactone (ω-PDL) based polymers is increased by copolymerization with a smaller branched lactone, δ-undecalactone (δ-UDL). The copolyester microstructure was assessed by 13C NMR/MALDI-ToF MS and indicates a block-like or random-like structure depending on the feed ratio. DSC analysis reveals a considerable decrease in the crystallinity of the copolyesters which can be attributed to the lack of stereoselectivity of the alkyl substituent of δ-UDL hampering chain packing. Consequently, the ω-PDL-based copolyesters present a broader solubility range towards polar aprotic solvents as demonstrated by the Hansen solubility parameter analysis. Finally, the effect of the ring size and position of the substituents of the comonomer lactone on the solubility range of ω-PDL-based copolyesters was investigated by copolymerization with a β,δ-substituted-ε-caprolactone. This broadening of the solubility range of ω-PDL-based copolyesters should enable the use of this biobased macrolactone in applications such as additives in coatings.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...