Radical polymerization in the presence of a peroxide monomer: an approach to branched vinyl polymers†
Abstract
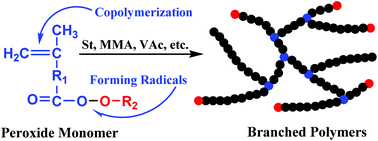
In this paper, we report radical polymerization in the presence of a peroxide monomer for the preparation of branched vinyl polymers. The peroxide monomer, tert-butyl peroxyacetate methacrylate (BPAMA), was designed and prepared in high purity from commercially available reagents via classic organic reactions. Triple-detection size-exclusion chromatography (TD-SEC) measurements, NMR analyses, and hydrolysis experiments were used to reveal the polymerization procedure and to confirm the branching structure of the prepared polymers. Branched polymers of styrene, methyl methacrylate (MMA), and vinyl acetate (VAc) were prepared under solvent-free conditions through radical polymerization in the presence of a peroxide monomer. Furthermore, radical polymerization in the presence of the peroxide monomer can be operated in a simple polymerization composition involving only the peroxide monomer BPAMA with MMA or VAc. The obtained branched polymers exhibited high molecular weights (Mw.MALLS > 106 g mol−1) and relatively narrow molecular weight distributions (2.5 ≤ PDI ≤ 6.8). Generally, radical polymerization in the presence of a peroxide monomer as the initiator and the branching agent can make the preparation of branched vinyl polymers almost equally as facile as the preparation of their linear analogs. This approach is applicable to a wide variety of monomers and can be performed with a simple polymerization composition in the bulk under moderate conditions compared with the reported strategies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...