A novel post-polymerization modification route to functional poly(disubstituted acetylenes) through phenol–yne click reaction†
Abstract
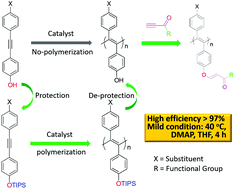
We report a new synthetic strategy to derive functional poly(disubstituted acetylenes) (PDSAs) through “phenol–yne click reaction”. The phenol-containing PDSA was prepared by the polymerization of the triisopropylsilane (TIPS)-protected 4-((4-fluorophenyl)ethynyl)phenol monomer and by a subsequent de-protection step. Then, different functional groups (e.g., ester and amide) were grafted onto the PDSA side chains via the highly efficient “phenol–yne click reaction”. The post-polymerization modification was carried out under mild conditions (at 40 °C, in common solvent) under an air atmosphere for a short time (4 h). The structures of the products were well characterized by GPC, NMR, and FTIR techniques and satisfactory data were collected. The data indicated that the phenol groups on the precursor PDSA were highly active to react with activated acetylenic compounds bearing functional groups intolerable to direct polymerization. This is the first example of the preparation of phenol-containing PDSA and the use of it as a precursor to prepare functional PDSAs. Besides the activated ester, thiol–ene click reaction, Michael addition reaction and Cu(I) catalysed alkyne–azide click reaction, we added a new tool in the tool-box for the synthesis of functional polymers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...