Scalable synthesis of organic-soluble carbon quantum dots: superior optical properties in solvents, solids, and LEDs†
Abstract
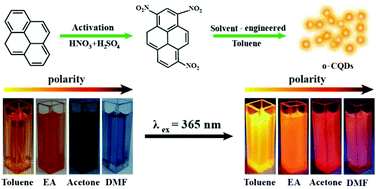
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) have attracted much attention owing to their unique optical properties and a wide range of applications. The fabrication and control of CQDs with organic solubility and long-wavelength emission are still urgent issues to be addressed for their practical use in LEDs. Here, organic-soluble CQDs were produced at a high yield of ∼90% by a facile solvent engineering treatment of 1,3,6-trinitropyrene, which were simultaneously used as the nitrogen and carbon sources. The optical properties of the organic-soluble CQDs (o-CQDs) were investigated in nonpolar and polar solvents, films, and LED devices. The CQDs have a narrow size distribution around 2.66 nm, and can be dispersed in different organic solvents. Significantly, the as-prepared CQDs present an excitation-independent emission at 607 nm with fluorescence quantum yields (QYs) up to 65.93% in toluene solution. A pronounced solvent effect was observed and their strong absorption bands can be tuned in the whole visible region (400–750 nm) by changing the solvent. The CQDs in various solvents can emit bright, excitation-independent, long-wavelength fluorescence (orange to red). Furthermore, benefiting from the unique oil-solution properties, the as-prepared CQDs can be processed in thin film and device forms to meet the requirements of various applications, such as phosphor-based white-light LEDs. The color coordinate for these CQD modified LEDs is realized at (0.32, 0.31), which is close to pure white light (0.33, 0.33).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...