Distinguishing thermal lens effect from electronic third-order nonlinear self-phase modulation in liquid suspensions of 2D nanomaterials†
Abstract
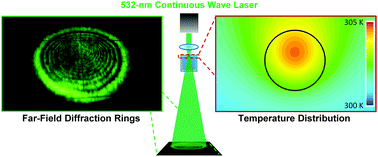
The interaction of light with atomically thin nanomaterials has attracted enormous research interest in order to understand two-dimensional (2D) electron systems and develop novel opto-electronic devices. The observations of spatial self-phase modulation and the associated multiple diffraction ring patterns in liquid suspensions of 2D nanomaterials are believed to be excellent examples of strong laser interaction with 2D nanomaterials and this phenomenon has been attributed to their large electronic third-order susceptibilities. By performing a series of control experiments with liquid suspensions of graphene and graphene oxide flakes in different solvents at various temperatures under an increasing modulation frequency of laser illumination, we first show that the diffraction ring pattern has little dependence on the type of nanomaterial but strongly depends on the duration of laser illumination. A laser induced local refractive index change is then monitored by a weaker probe beam, resulting in the divergent diffraction of the probe beam that indicates a lower self-induced refractive index in the center of the pump laser beam than at its periphery: a clear signature of the thermal lens effect. Finally, we use computational fluid dynamics to simulate laser induced temperature and index changes of the suspensions. The evolution of diffraction rings is well correlated to the transient temperature distribution. Our understanding of complex laser interactions with nanomaterial suspensions and the associated thermal lens effect paves the way for further basic studies and fluid opto-electronic applications of 2D nanomaterials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...