Phenylboronic acid-functionalized core–shell magnetic composite nanoparticles as a novel protocol for selective enrichment of fructose from a fructose–glucose aqueous solution
Abstract
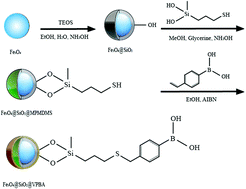
We developed an efficient and mild method for the preparation of boronic acid-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), and the selective separation of fructose from a sample solution was demonstrated for the first time. A modified hydrothermal method was chosen to prepare the naked Fe3O4 MNPs, and then the Fe3O4@SiO2 MNPs were synthesized by a sol–gel reaction. After that, the thiol-coated Fe3O4 MNPs were synthesized by a sol–gel reaction with an organosilicon coupling agent. Finally, the thiol groups on the surface of the MNPs served as clickable sites to react with 4-vinylphenylboronic acid (VPBA) via a thiol–ene (TE) click reaction to obtain the final MNPs with a high density of boronic acid ligands immobilized on the surface. It is known that phenylboronic acid ligands on Fe3O4@SiO2@VPBA MNPs can form stable five- or six-membered cyclic esters with cis-diol-containing molecules. In this work, the click-Fe3O4 MNPs with a mean diameter of 195 nm exhibited high selectivity and binding capacity towards fructose. Also, the adsorption efficiency of fructose could reach ≈96% under optimum adsorption conditions. In addition, the adsorption efficiency of fructose was about six times higher than that of glucose in a fructose–glucose aqueous solution, suggesting that the resultant Fe3O4@SiO2@VPBA MNPs had higher affinity for fructose under the interference of competing glucose. Reusability is also an important factor of affinity adsorbents, and the adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@SiO2@VPBA MNPs was virtually unchanged after six cycles of reuse.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...